Integrating with AWS CodePipeline
Create an IAM role for the AWS CodeBuild
To set up AWS CodeBuild to work with the Amazon EKS cluster, you need the AWS AccountID to modify aws-auth configmap. AWS CodeBuild requires an IAM role capable of deploying to the Workload EKS cluster. You can set that up by entering these commands in succession on the AWS Cloud9 Amazon Linux machine:
# Create the IAM role for CodeBuild to deploy to Amazon EKS
TRUST="{ \"Version\": \"2012-10-17\", \"Statement\": [ { \"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": { \"AWS\": \"arn:aws:iam::${ACCOUNT_ID}:root\" }, \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\" } ] }"
echo '{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "eks:Describe*", "Resource": "*" } ] }' > /tmp/iam-role-policy
aws iam create-role --role-name AquaWorkshopCodeBuildKubectlRole --assume-role-policy-document "$TRUST" --output text --query 'Role.Arn'
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name AquaWorkshopCodeBuildKubectlRole --policy-name eks-describe --policy-document file:///tmp/iam-role-policy
# Finally, modify the aws-auth configmap to map the IAM role in the kubeconfig file:
ROLE=" - rolearn: arn:aws:iam::$ACCOUNT_ID:role/AquaWorkshopCodeBuildKubectlRole\n username: build\n groups:\n - system:masters"
kubectl get -n kube-system configmap/aws-auth -o yaml | awk "/mapRoles: \|/{print;print \"$ROLE\";next}1" > /tmp/aws-auth-patch.yml
kubectl patch configmap/aws-auth -n kube-system --patch "$(cat /tmp/aws-auth-patch.yml)"Fork the sample GitHub Repo
We have provided a sample Go application and the AWS CloudFormation template you need for the next steps in our sample GitHub repository: https://github.com/rycb4r/amazon-eks-devsecops. Fork this sample repository using your GitHub account, and create a GitHub access token.
Generate a GitHub token to use in CloudFormation
A Personal Access Token can be generated by going to Settings > Developer Settings > Personal access token or click here Generate a new token for this workshop.
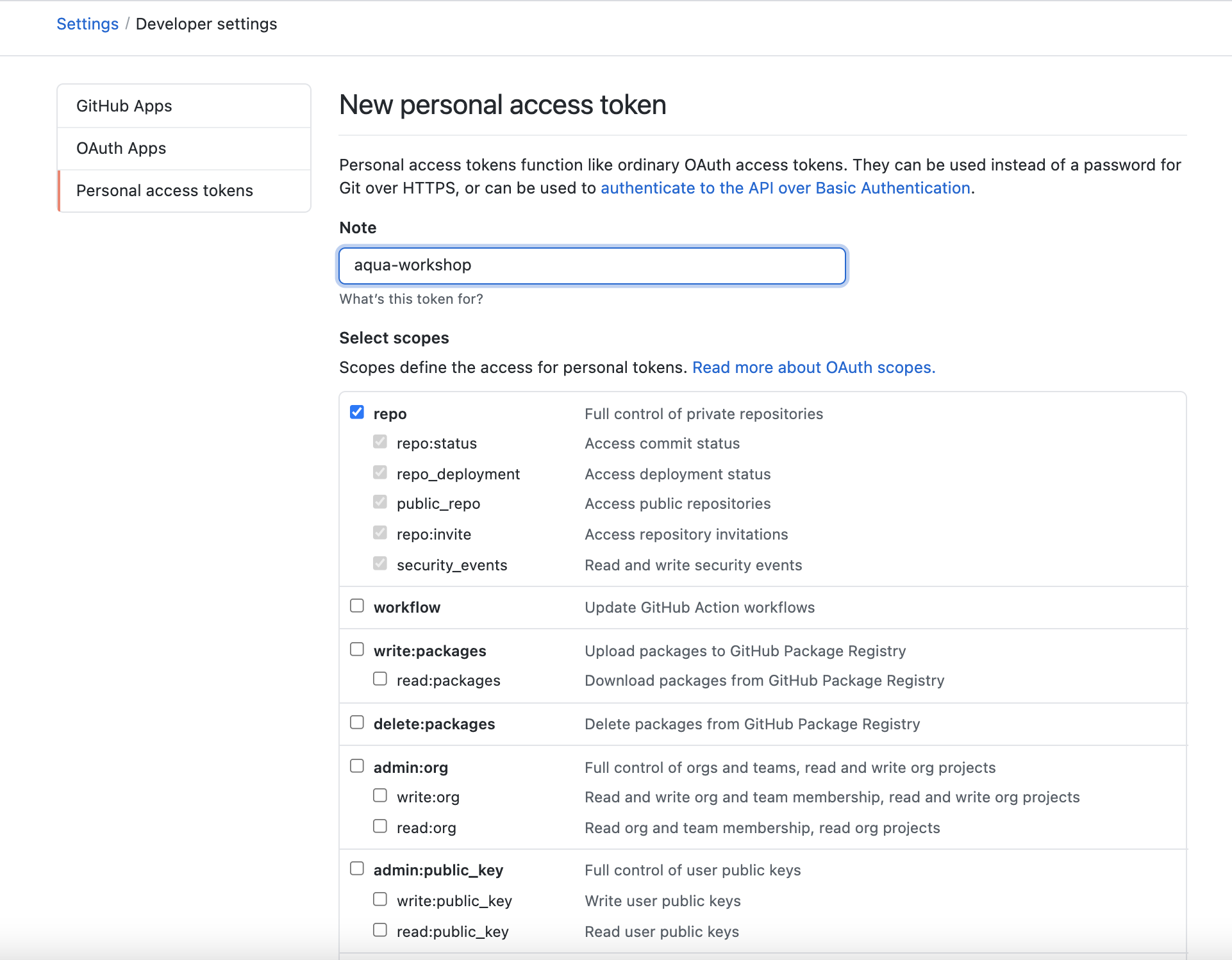
Copy the token

Deploy the Aqua and AWS CodePipeline integration
Click the Launch button to create the CloudFormation stack in the AWS Management Console.
| Launch template | ||
|---|---|---|
| CodePipeline & Aqua | Launch | Download |

Enable static scanning
“scannercli” is an Aqua binary that scans the image locally as soon as it’s built, and then communicates back to the Aqua CSP server to compare the findings with Aqua’s CyberCenter. Pertaining to the security tolerance level, the build can be passed or failed based on the scanning results.
The reports are stored as an AWS CodePipeline artifact in the Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket, and can be easily retrieved from the AWS Management Console itself.
To enable automated static scanning of the build artifacts, scannercli is used in the buildspec.yml (https://github.com/aquasecurity/amazon-eks-devsecops/blob/master/buildspec.yml#L19) in the build stage as shown here:
yaml build:
commands:
- docker build --tag $REPOSITORY_URI:$TAG .
- ./scannercli scan --host $AQUA_URL --user $AQUA_USER --password $AQUA_PASSWORD --register-compliant --local $REPOSITORY_URI:$TAG --no-verify --htmlfile aqua.html
- docker push $REPOSITORY_URI:$TAG