Block Container Exec
The easiest way to gain access to a running container and executing commands against it is kubectl exec
Attackers with permissions could run kubectl exec to execute malicious code and compromise resources within a cluster.
Aqua has a security control that prevents an attacker from gaining any form of shell access to running containers.
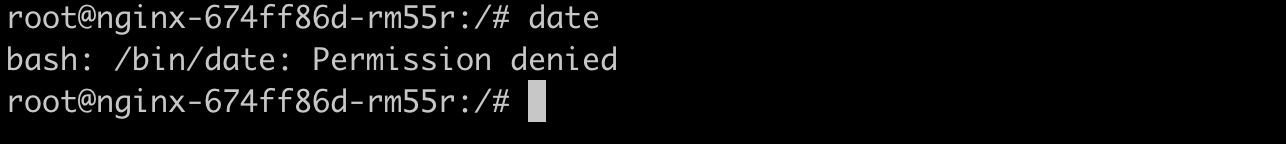
kubectl exec -it <pod_name> bashAs you can see Aqua blocks this attempt successfully.

Let’s go ahead and remove this security control for the runtime policy so that we can move on to Drift Prevention.
Navigate to Policies > Runtime Policies > Aqua default runtime policy and remove the control for Block Container Exec.
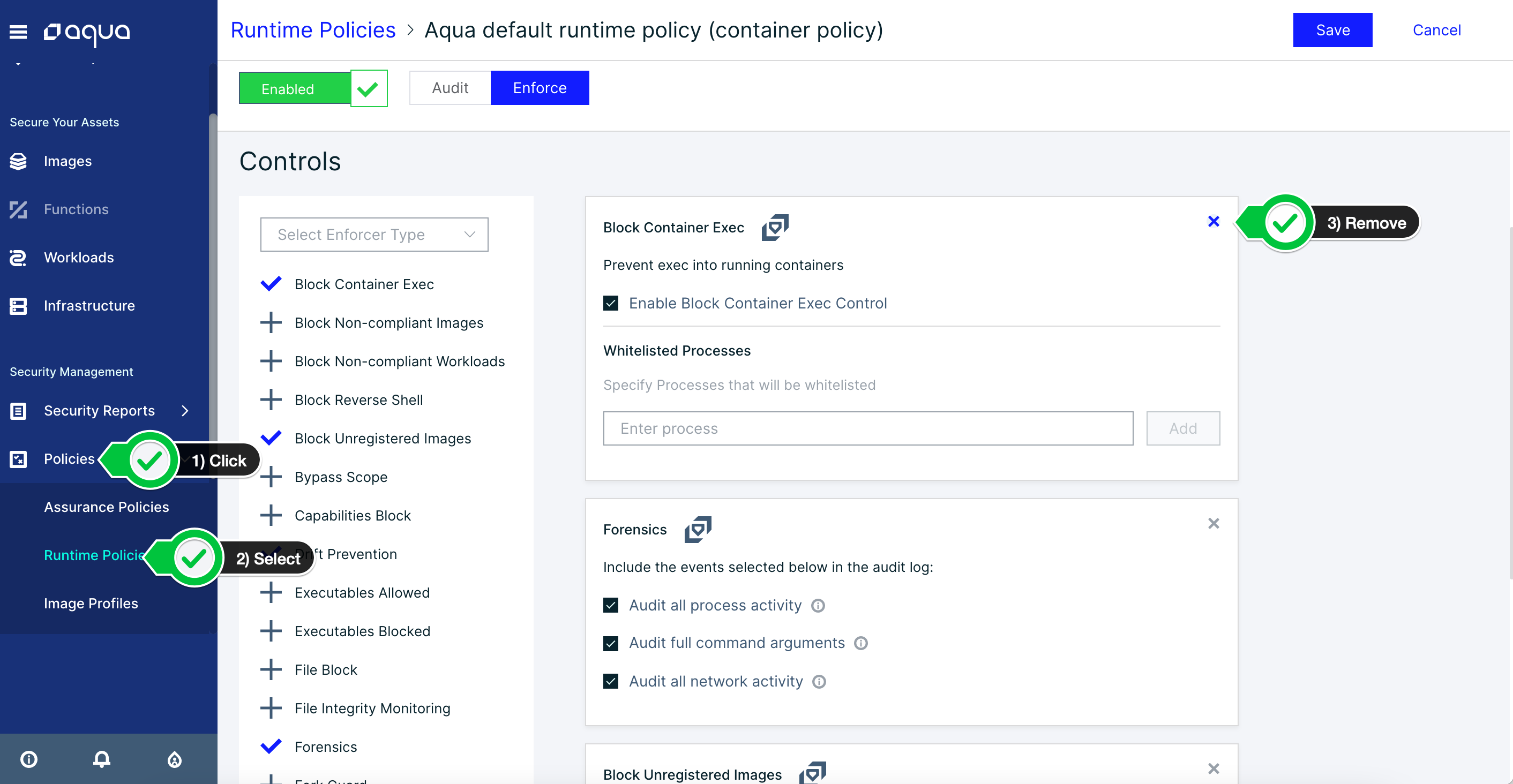
We can also add a new control to block a certain executable date

Now let’s exec into the running nginx container. We can do that now because we disabled the Block Container Exec control.
kubectl exec -it <pod_name> bashNotice that we are now in the nginx container as the root user (something else that can be prevented by Aqua). As such, there’s nothing we should not be able to do. However, if we try executing the date executable, we will get a Permission denied error message. This is because Aqua blocked that executable from running.